In the realm of single-board computers, two names stand out: the Libre Computer Board and the Raspberry Pi. Both have made a significant impact in the DIY electronics world, offering affordable yet powerful computing solutions.
But when it comes to choosing between the two, which one emerges as the superior option? The Libre Computer Board, with its impressive performance metrics, is often hailed as a robust upgrade to the Pi 3B+. On the other hand, the Raspberry Pi has an unrivaled community support and software ecosystem.
This article aims to delve deep into the comparison between these two titans and help you make an informed decision.
What Is the Raspberry Pi?

Key Features of Raspberry Pi:
- Compact Form Factor: Raspberry Pi boards are small and compact, roughly the size of a credit card. This makes them highly portable and suitable for projects with space constraints;
- Affordability: One of the most notable features of Raspberry Pi is its affordability. These boards are priced competitively, making them accessible to students, hobbyists, and enthusiasts with limited budgets;
- Broad Compatibility: Raspberry Pi devices are compatible with a variety of peripherals and accessories. They feature a 40-pin GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output) header that allows users to connect sensors, displays, cameras, and other external components;
- Operating System Support: Raspberry Pi officially supports Raspberry Pi OS (formerly Raspbian), a Linux-based operating system optimized for Pi hardware. However, it also has extensive support for other Linux distributions, including Ubuntu and Debian;
- Processor Power: Raspberry Pi models have evolved over the years, with the latest Raspberry Pi 4 featuring a powerful Broadcom BCM2711 quad-core Cortex-A72 CPU. This improved processing power allows for a wide range of applications, including multimedia and light gaming;
- Video Output: Raspberry Pi boards typically feature HDMI ports for video output, allowing users to connect to displays, monitors, or TVs. The Raspberry Pi 4, for example, supports dual 4K displays at 60Hz;
- Wireless Connectivity: Recent Raspberry Pi models, such as the Raspberry Pi 4, come equipped with dual-band 802.11ac Wi-Fi and Bluetooth 5.0 support. This wireless connectivity enhances their versatility in various IoT and networking projects;
- Community Support: Raspberry Pi has one of the largest and most active SBC communities worldwide. The community provides extensive resources, forums, tutorials, and a wealth of third-party projects and add-ons [2];
Pros of Raspberry Pi:
- Accessibility: Raspberry Pi’s low cost makes it accessible to a wide range of users, including students, educators, and hobbyists;
- Education: It was initially designed to promote computer science education, making it an ideal tool for learning programming and electronics;
- Versatility: Raspberry Pi can be used for diverse applications, including home automation, media centers, retro gaming, robotics, and more;
- Vast Community: The large and active Raspberry Pi community provides extensive support, including forums, tutorials, and a wealth of user-contributed projects;
- Extensive Accessory Ecosystem: Raspberry Pi has a vast ecosystem of official and third-party accessories, including HATs (Hardware Attached on Top), camera modules, and displays
- Regular Updates: The Raspberry Pi Foundation continues to release new models with improved hardware specifications, ensuring that users have access to the latest technology;
Cons of Raspberry Pi:
- Limited Processing Power: While recent models have improved processing power, Raspberry Pi may not be suitable for resource-intensive tasks and high-performance computing;
- Limited RAM: Raspberry Pi models typically offer 2GB, 4GB, or 8GB of RAM, which can be limiting for memory-intensive applications;
- Non-x86 Architecture: Raspberry Pi uses an ARM-based architecture, which may require software optimization or compatibility adjustments for some applications designed for x86 systems;
- Storage: The primary storage medium for Raspberry Pi is a microSD card, which may not provide the speed and reliability of solid-state drives (SSDs) or hard drives;
- Peripheral Limitations: While Raspberry Pi offers GPIO pins for connecting external components, the number and types of available pins may not be sufficient for complex projects;
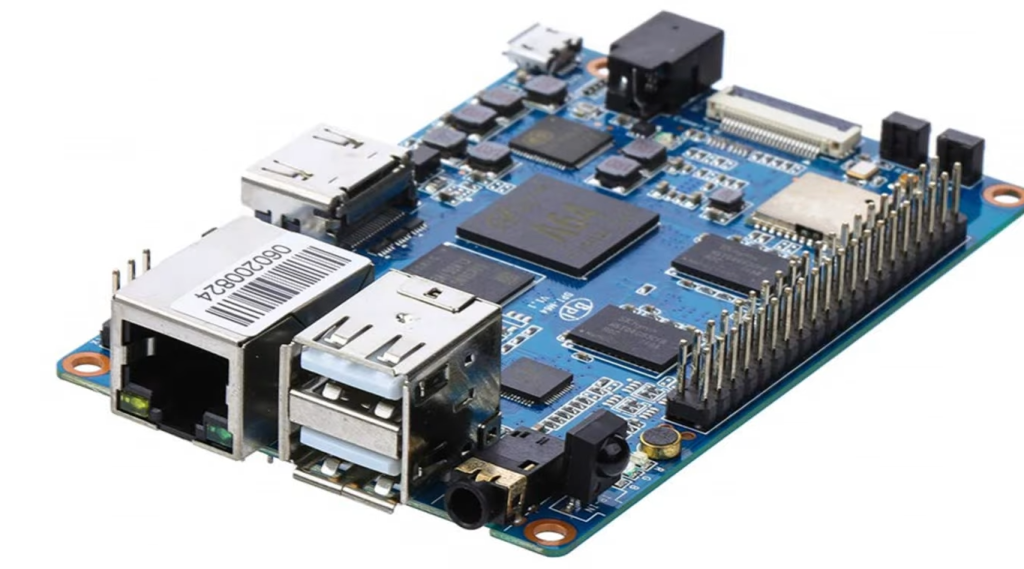
What is the Libre Computer Board?
The Libre Computer Board, often referred to as Libre Computer or Libre Computer Project, is a series of single-board computers (SBCs) developed by Shenzhen Libre Technology Co., Ltd. [3], a company specializing in open-source hardware and software solutions.
Libre Computer Boards are designed to provide users with powerful, versatile, and open-source computing platforms suitable for a wide range of applications, from IoT (Internet of Things) projects to multimedia applications and more.
Key Features of Libre Computer Board:
- Hardware Options: Libre Computer offers a variety of hardware options within its product lines, such as the Renegade series, La Frite series, and others. These options cater to different use cases and performance requirements, providing users with choices in terms of CPU, GPU, RAM, and connectivity;
- Processor Power: Depending on the specific model, Libre Computer Boards are equipped with processors from Rockchip, Amlogic, and other manufacturers. These processors offer competitive processing power, suitable for a wide range of applications;
- Video Output: Many Libre Computer Board models support high-definition video output, with some models capable of dual 4K video output. This makes them suitable for multimedia applications, including media centers and digital signage;
- Wireless Connectivity: Libre Computer Boards often come with built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth options, including dual-band Wi-Fi support (2.4GHz and 5GHz). This enables wireless connectivity for IoT and networking projects;
- Operating System Compatibility: Libre Computer Boards typically support popular Linux distributions, including Ubuntu, Debian, and Armbian. Some models, such as the ROC-RK3399-PC, even offer official Android support, providing users with a choice of operating systems;
- Customizability: The Libre Computer Project emphasizes open-source hardware and software, allowing users to modify and customize their boards to suit their specific project requirements. This open approach encourages experimentation and innovation;
- Community Support: While the Libre Computer community may be smaller than that of the Raspberry Pi, it is active and provides valuable support through forums, wikis, and online resources;
Pros of Libre Computer Board:
- Hardware Flexibility: The variety of hardware options within the Libre Computer Board series allows users to select a board that precisely matches their project’s requirements, whether it’s a low-power IoT application or a high-performance multimedia project;
- Processing Power: Libre Computer Boards are equipped with processors that provide competitive processing power, making them suitable for a wide range of computational tasks;
- High-Quality Video Output: Many Libre Computer Board models support high-definition video output, including dual 4K options, making them ideal for multimedia and media center applications;
- Wireless Connectivity: Built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth options, including dual-band support, enhance the wireless connectivity capabilities of Libre Computer Boards for IoT and networking projects;
- Open-Source Approach: Libre Computer Project’s commitment to open-source hardware and software encourages users to customize and modify their boards, fostering innovation and experimentation;

Cons of Libre Computer Board:
- Smaller Community: The Libre Computer community, while active and supportive, is smaller than that of more widely recognized SBCs like the Raspberry Pi. This may result in fewer resources and third-party projects;
- Complexity for Beginners: The wide range of hardware options and customization possibilities can be overwhelming for beginners. Users with limited experience may find it challenging to choose the right board and configure it for their needs;
- Availability of Accessories: While Libre Computer Boards are compatible with some Raspberry Pi accessories, they may have a more limited ecosystem of official and third-party accessories and add-ons compared to the Raspberry Pi;
- Operating System Compatibility: Although Libre Computer Boards support popular Linux distributions, some users may prefer the familiarity and extensive support of Raspberry Pi OS (formerly Raspbian) for their projects;
Libre Computer Board vs. Raspberry Pi: Compare The Specs
Hardware Options
Both Libre Computer Board and Raspberry Pi offer a range of hardware options to cater to diverse user requirements. However, Libre Computer Board is renowned for providing more flexibility in terms of hardware configurations [4]. While Raspberry Pi primarily focuses on specific models, Libre Computer Board offers various product lines, each with multiple options.
Libre Computer Board’s hardware options include the Renegade series, La Frite series, and the ROC-RK3399-PC. These options vary in terms of CPU, GPU, RAM, and other features, allowing users to choose a board that precisely matches their needs.
Raspberry Pi, on the other hand, traditionally releases models such as the Raspberry Pi 4, 3B+, and Zero. While these models have served a wide range of applications well, they offer fewer hardware variations compared to Libre Computer Board.
CPU/GPU/RAM
Libre Computer Board:
- The “Renegade” series offers boards with Rockchip RK3328 and Amlogic S905X2 CPUs, providing excellent processing power for various tasks;
- La Frite series features the Amlogic S805X2 CPU, which is suitable for less demanding applications;
- ROC-RK3399-PC boasts the powerful Rockchip RK3399 processor, making it suitable for intensive computing tasks;
- RAM options of Libre models range from 1GB to 4GB, allowing users to choose the right amount for their projects;
Raspberry Pi:
- Raspberry Pi 4 is equipped with a Broadcom BCM2711 quad-core Cortex-A72 CPU, making it significantly more powerful than its predecessors;
- GPU capabilities are also impressive, with VideoCore VI handling graphics efficiently;
- Raspberry Pi 4 comes in 2GB, 4GB, and 8GB RAM variants, offering flexibility in memory allocation;
In terms of CPU and GPU performance, Libre Computer Board’s ROC-RK3399-PC and Raspberry Pi 4 are closely matched, but Libre Computer Board provides more options for users with different processing requirements.

Video Output
Video output options are essential for SBCs used in multimedia projects or as media centers. Both Libre Computer Board and Raspberry Pi offer HDMI ports for connecting to displays.
Libre Computer Board:
- Some models, like ROC-RK3399-PC, support dual 4K video output, making them suitable for high-definition multimedia applications;
- The Renegade series also provides excellent video quality with support for 4K resolution;
Raspberry Pi:
- Raspberry Pi 4 offers dual micro-HDMI ports that support dual 4K displays at 60Hz;
- Older Raspberry Pi models support varying levels of video output quality, with 1080p being a common standard;
If you require high-quality video output for your project, both Libre Computer Board and Raspberry Pi 4 are capable choices. However, Libre Computer Board’s ROC-RK3399-PC stands out for its dual 4K support.
Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
Wireless connectivity is crucial for many SBC projects, especially those involving IoT devices or remote control. Both Libre Computer Board and Raspberry Pi offer built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth options, but the specifics vary:
Libre Computer Board:
- Models like ROC-RK3399-PC and Renegade series often come with dual-band Wi-Fi (2.4GHz and 5GHz) and Bluetooth 4.2 support;
- La Frite series may have variations in terms of wireless capabilities, depending on the specific model;
Raspberry Pi:
- Raspberry Pi 4 features dual-band 802.11ac Wi-Fi and Bluetooth 5.0 support, offering faster and more reliable wireless connections;
- Older Raspberry Pi models have varying Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities, with some models supporting only 2.4GHz Wi-Fi [5];
For users who prioritize faster wireless connections and Bluetooth 5.0 compatibility, Raspberry Pi 4 has the edge in this category. However, Libre Computer Board provides satisfactory wireless options for most projects.
Input/Output Pins
Both Libre Computer Board and Raspberry Pi are equipped with GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output) pins, allowing users to connect various sensors, displays, and other peripherals. These pins are essential for DIY electronics projects and prototyping.
Libre Computer Board:
The Renegade series and ROC-RK3399-PC come with a 40-pin GPIO header, similar to the Raspberry Pi’s GPIO pinout.
Raspberry Pi:
Raspberry Pi models, including the Raspberry Pi 4, feature a 40-pin GPIO header, providing compatibility with a wide range of accessories and HATs (Hardware Attached on Top).
In terms of GPIO pins, both Libre Computer Board and Raspberry Pi offer similar capabilities, making them suitable choices for electronic projects.
Ports
The availability of ports on an SBC can greatly impact its usability for various applications.
Libre Computer Board:
- ROC-RK3399-PC includes USB 3.0 and USB 2.0 ports, Gigabit Ethernet, and a USB Type-C port for power and data;
- The “Renegade” series offers a variety of port configurations, including USB 3.0, USB 2.0, and Ethernet options;
- La Frite series may have fewer ports, depending on the specific model;
Raspberry Pi:
- Raspberry Pi 4 comes with two USB 3.0 ports, two USB 2.0 ports, Gigabit Ethernet, and two micro-HDMI ports for video output;
- Older Raspberry Pi models have varying port configurations, with some featuring only USB 2.0 ports and HDMI output;
In terms of port options, Raspberry Pi 4 has a slight advantage with its USB 3.0 ports, which offer faster data transfer speeds compared to USB 2.0. However, the specific requirements of your project will determine which port configuration is more suitable.
Storage
Storage options are essential for SBCs, as they determine how much data you can store and access. Both Libre Computer Board and Raspberry Pi support microSD card storage, but they also have some variations:
Libre Computer Board:
- ROC-RK3399-PC provides an eMMC flash storage option in addition to the microSD card slot, offering faster and more reliable storage performance;
- Other models in the Libre Computer Board lineup primarily rely on microSD cards for storage;
Raspberry Pi:
Raspberry Pi models, including the Raspberry Pi 4, use microSD cards as the primary storage medium. However, some users choose to boot from USB-connected storage devices for improved performance.
If you prioritize faster storage options, Libre Computer Board’s ROC-RK3399-PC with its eMMC storage support might be more appealing. However, both SBCs can benefit from booting from external storage devices for improved performance and reliability.
OS Compatibility
The availability of compatible operating systems is crucial for any SBC, as it determines the software ecosystem you can access.
Libre Computer Board:
Libre Computer Board typically supports popular Linux distributions like Ubuntu, Debian, and Armbian.
ROC-RK3399-PC has official Android support in addition to Linux-based OS options.
Raspberry Pi:
- Raspberry Pi officially supports Raspberry Pi OS (formerly Raspbian), a Linux-based OS optimized for the Pi’s hardware;
- There is also a wide range of community-supported operating systems available for Raspberry Pi, including Ubuntu, Debian, and various IoT-focused distributions;
Both Libre Computer Board and Raspberry Pi have extensive OS compatibility, so your choice should be based on your specific project requirements and familiarity with the available OS options.
Size
The physical size of an SBC can be a crucial factor depending on the intended use.
Libre Computer Board:
- Libre Computer Board models vary in size, but they are generally compact and comparable to Raspberry Pi in terms of dimensions;
- ROC-RK3399-PC, one of the larger models, measures approximately 100mm x 60mm [6];
Raspberry Pi:
Raspberry Pi models, including the Raspberry Pi 4, have a standard size of approximately 85.6mm x 56.5mm.
In terms of size, both Libre Computer Board and Raspberry Pi are compact and suitable for a wide range of applications. However, if space constraints are a concern, Raspberry Pi’s slightly smaller form factor might be advantageous.
Software Support
Software support is a crucial aspect of any SBC, as it determines the availability of applications and libraries for your projects.
Libre Computer Board:
- Libre Computer Board offers official software support for various Linux distributions, making it a great choice for developers and enthusiasts;
- ROC-RK3399-PC has official Android support in addition to Linux-based OS options;
- The LibreELEC community provides support for Libre Computer Board devices, making them suitable for media center and Kodi-based projects;
Raspberry Pi:
- Raspberry Pi OS (formerly Raspbian) is the official operating system optimized for Raspberry Pi hardware;
- The Raspberry Pi community is vast, and many third-party developers provide software and libraries for various applications
- Raspberry Pi has extensive support for educational and programming tools;
Both Libre Computer Board and Raspberry Pi enjoy strong software support from their respective communities. However, Raspberry Pi’s dedicated educational and programming resources give it a slight edge for users interested in teaching and learning opportunities.

Hardware Support
The availability of accessories and add-ons can greatly enhance the functionality of an SBC.
Libre Computer Board:
- Libre Computer Board has a growing ecosystem of accessories and add-ons, including cases, power supplies, and cooling solutions;
- The compatibility of Libre Computer Board with some Raspberry Pi accessories adds to its versatility;
Raspberry Pi:
- Raspberry Pi has an extensive ecosystem of official and third-party accessories, including HATs (Hardware Attached on Top), camera modules, and displays;
- The Raspberry Pi Foundation offers a wide range of official cases, power supplies, and other peripherals;
While both SBCs have a variety of hardware options, Raspberry Pi’s well-established ecosystem provides more choices when it comes to accessories and add-ons.
Connectivity
Connectivity options are crucial for various SBC applications, including networking and data transfer.
Libre Computer Board:
- ROC-RK3399-PC offers Gigabit Ethernet for fast wired networking;
- Dual-band Wi-Fi (2.4GHz and 5GHz) and Bluetooth support provide wireless connectivity options;
- USB ports allow for connecting a wide range of peripherals;
Raspberry Pi:
- Raspberry Pi 4 features Gigabit Ethernet for wired networking, providing faster data transfer speeds compared to its predecessors;
- Dual-band Wi-Fi (2.4GHz and 5GHz) and Bluetooth 5.0 offer robust wireless connectivity options;
- USB ports allow for connecting peripherals, and the USB 3.0 ports provide faster data transfer;
In terms of connectivity, both SBCs offer similar options, with Raspberry Pi 4 boasting faster Gigabit Ethernet and USB 3.0 support.
Processing Power
Processing power is a critical factor for SBCs used in tasks that require computational strength.
Libre Computer Board:
- ROC-RK3399-PC features the Rockchip RK3399 processor, which provides powerful CPU and GPU performance;
- The “Renegade” series offers varying levels of processing power, depending on the specific model and CPU choice;
- La Frite series, while less powerful, is suitable for less demanding applications;
Raspberry Pi:
- Raspberry Pi 4 is equipped with the Broadcom BCM2711 quad-core Cortex-A72 CPU, offering substantial processing power;
- The GPU capabilities of Raspberry Pi 4, with VideoCore VI, contribute to its multimedia performance;
In terms of processing power, both Libre Computer Board’s ROC-RK3399-PC and Raspberry Pi 4 offer competitive options. However, Libre Computer Board’s broader range of CPU choices provides more flexibility for users with specific performance requirements.
Community
The strength of a community around an SBC can greatly influence its long-term support and availability of resources.
Libre Computer Board:
- Libre Computer Board has a growing community of users and developers who contribute to forums, wikis, and online resources;
- While the community is smaller than Raspberry Pi’s, it is active and provides valuable support;
Raspberry Pi:
- Raspberry Pi has one of the largest and most active SBC communities in the world. It includes forums, official documentation, educational resources, and a wide range of third-party projects and tutorials;
- The Raspberry Pi Foundation actively supports educational initiatives and outreach programs;
In terms of community support, Raspberry Pi’s well-established and vast community is a significant advantage.м The abundance of resources and tutorials available for Raspberry Pi makes it an excellent choice for beginners and experienced users alike [7].

Libre Computer Board vs. Raspberry Pi: What To Choose?
Your choice between the Libre Computer Board and Raspberry Pi should be guided by the following questions:
- What is the primary purpose of your SBC project?
- Do you require high processing power for computational tasks?
- Will your project involve multimedia and high-definition video output?
- Is wireless connectivity (Wi-Fi and Bluetooth) essential for your project?
- Do you need a compact form factor for space-constrained applications?
- Are you comfortable with Linux-based operating systems?
Choosing between the Libre Computer Board and Raspberry Pi ultimately depends on your project’s specific requirements and your personal preferences. Consider factors such as hardware customizability, processing power, video output capabilities, wireless connectivity, operating system compatibility, and community support when making your decision.
Choose the Libre Computer Board if you need:
- Customizable hardware configurations;
- High processing power for specific computational tasks;
- Dual 4K video output for multimedia applications;
- Satisfactory wireless connectivity options;
- Flexibility in choosing from various Linux-based operating systems;
- Active yet smaller community support [8];
FAQ:
1. Is Libre computer the same as Raspberry Pi?
No, Libre Computer is not the same as Raspberry Pi. While both Libre Computer and Raspberry Pi are single-board computers (SBCs), they are developed by different organizations and have distinct hardware, specifications, and ecosystems.
Libre Computer offers a range of SBCs with various hardware options, while Raspberry Pi is a specific line of SBCs developed by the Raspberry Pi Foundation. They differ in terms of processor, GPU, form factor, community support, and accessories.
2. Is there anything better than a Raspberry Pi?
Whether something is “better” than a Raspberry Pi depends on specific use cases and requirements. Several SBCs offer similar or even superior specifications compared to Raspberry Pi in terms of processing power, RAM, and connectivity [9]. Examples include the NVIDIA Jetson series for AI and robotics applications or the Odroid series for general-purpose computing. The choice of SBC should be based on the project’s needs and budget.
3. Is Libre computer board compatible with Raspberry Pi?
Libre Computer boards are generally not fully compatible with Raspberry Pi. While they share some similarities in terms of form factor and GPIO pinouts, the hardware components and architecture can vary significantly between the two. Therefore, software and accessories designed specifically for Raspberry Pi may not work seamlessly with Libre Computer boards.
4. Do professionals use Raspberry Pi?
Yes, professionals use Raspberry Pi in a variety of fields. Raspberry Pi is widely used by professionals in industries such as education, IoT development, automation, robotics, prototyping [10], and more. It serves as an affordable and versatile platform for a wide range of applications, making it popular among both beginners and experienced professionals.
5. What is the fastest single-board computer this year?
The fastest single-board computer can vary from year to year as new models are released. As of 2023, some of the fastest SBCs available included the NVIDIA Jetson Xavier NX, the Odroid-N2+, and the Raspberry Pi 4 (in its category).
6. Can Raspberry Pi run CAD?
Raspberry Pi can run CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, but its performance may be limited, especially for complex 3D CAD tasks. Software like FreeCAD and LibreCAD can be installed on Raspberry Pi to create 2D and 3D designs. For less resource-intensive CAD tasks, Raspberry Pi can be a viable option, but professionals may prefer more powerful hardware for demanding CAD work.
7. Can a Raspberry Pi run a CNC machine?
Yes, Raspberry Pi can be used to control a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine, such as a 3D printer or a CNC router, using appropriate software and hardware interfaces. Software like OctoPrint or CNC.js can be installed on a Raspberry Pi to manage and control CNC operations [11]. However, the suitability of Raspberry Pi for this purpose depends on the specific requirements of the CNC machine and the complexity of the tasks.
8. Why not to use Raspberry Pi?
While Raspberry Pi is a versatile and affordable SBC, there are some scenarios where it may not be the best choice:
- High-Performance Computing: For tasks requiring significant processing power or extensive RAM, Raspberry Pi may not provide the required performance;
- Resource-Intensive Applications: Resource-intensive applications like 3D rendering, complex simulations, or AI training may be better suited for more powerful hardware;
- Specific Hardware Requirements: If your project relies on specific hardware components that are not compatible with Raspberry Pi, you may need an alternative SBC;
- Commercial or Industrial Use: In some commercial and industrial settings, dedicated industrial computers may be preferred over SBCs like Raspberry Pi for reliability and longevity;
9. Does Raspberry Pi run faster on SSD?
Yes, Raspberry Pi can benefit from running on an SSD (Solid-State Drive) instead of an SD card in terms of read/write speeds and overall system responsiveness. By connecting an SSD via USB or SATA, users can significantly improve the data transfer rates and reduce SD card wear. However, the full-speed potential of an SSD may be limited by the USB interface or SATA-to-USB adapter used.
10. Is Raspberry Pi powerful enough for AI?
Raspberry Pi is capable of running AI (Artificial Intelligence) and machine learning workloads, particularly inference tasks, using frameworks like TensorFlow Lite and OpenCV. While it may not match the performance of high-end AI accelerators, it can handle many AI applications, including image recognition, object detection, and natural language processing.
For more demanding AI training tasks, more powerful hardware like NVIDIA Jetson series SBCs may be preferable.
11. How do you power a Libre computer board?
Libre Computer boards are typically powered using a micro-USB or USB-C port, similar to many other SBCs. Users can supply power using a compatible USB power adapter, a USB cable, and a power source such as a USB charger or a computer’s USB port [12]. It’s essential to check the board’s power requirements and use a power supply that meets or exceeds those specifications.
12. Can you install Raspbian on a Libre computer?
Raspbian, which has been renamed Raspberry Pi OS, is designed specifically for Raspberry Pi’s hardware architecture. As a result, it may not be compatible with Libre Computer boards due to differences in hardware components, architecture, and drivers. It is recommended to use an operating system that is officially supported and compatible with the specific Libre Computer board you are using.
13. How fast can Raspberry Pi write to an SD card?
The write speed of an SD card on a Raspberry Pi can vary depending on several factors, including the model of the Raspberry Pi, the quality of the SD card, and the file system being used. In general, write speeds on Raspberry Pi can range from a few MB/s to around 20-30 MB/s for high-quality SD cards. Using faster SD cards, optimizing the file system, and minimizing write operations can help improve write speeds.
14. What is the lifespan of a Raspberry Pi?
The lifespan of a Raspberry Pi can vary based on usage, environmental conditions, and the specific model. However, Raspberry Pi boards are designed for long-term use, and with proper care, they can last several years or more. The Raspberry Pi Foundation typically provides software updates and support for a reasonable duration after a model’s release.
Useful Video: I Can Save You Money! – Raspberry Pi Alternatives
References:
- https://www.electromaker.io/blog/article/raspberry-pi-3-vs-libre-computer-roc-rk3328-cc
- https://www.tomshardware.com/news/libre-computer-announces-sweet-potato-raspberry-pi-alternative
- https://www.zdnet.com/article/best-raspberry-pi-alternative/
- https://www.modernmakes.ca/blog/best-raspberry-pi-alternatives-2023
- https://www.howtogeek.com/36644/the-best-raspberry-pi-alternatives/
- https://beebom.com/best-raspberry-pi-4-alternatives/
- https://geekflare.com/best-raspberry-pi-alternatives/
- http://wiki.loverpi.com/specs:sbc:libre-aml-s805x-comparison-table
- https://pallavaggarwal.in/raspberry-pi-alternatives-clones/
- https://revolutionized.com/raspberry-pi-alternatives/
- https://linuxhint.com/cheap_raspberry_pi_alternatives/
- https://gl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Raspberry_Pi