Welcome to our comprehensive review of the Arduino Portenta H7, a powerful microcontroller board designed for industrial applications. This dual-core board, equipped with a 480 MHz ARM Cortex-M7 and a 240 MHz ARM Cortex-M4, promises high-performance computation capabilities [1].
But how does it fare in real-world usage? In this article, we’ll delve into the features, performance, and usability of the Arduino Portenta H7, helping you understand whether it’s the right fit for your project requirements. From its impressive processing speed to the open-source nature of its design, we’ll examine all aspects of this intriguing piece of hardware.
Arduino Portenta H7 Review:
In the ever-evolving landscape of embedded systems and microcontrollers, Arduino continues to be a formidable player. With each new release, Arduino consistently pushes the boundaries of what’s possible in the realm of electronics prototyping and development. One of its latest creations, the Arduino Portenta H7, is a testament to this commitment to innovation.
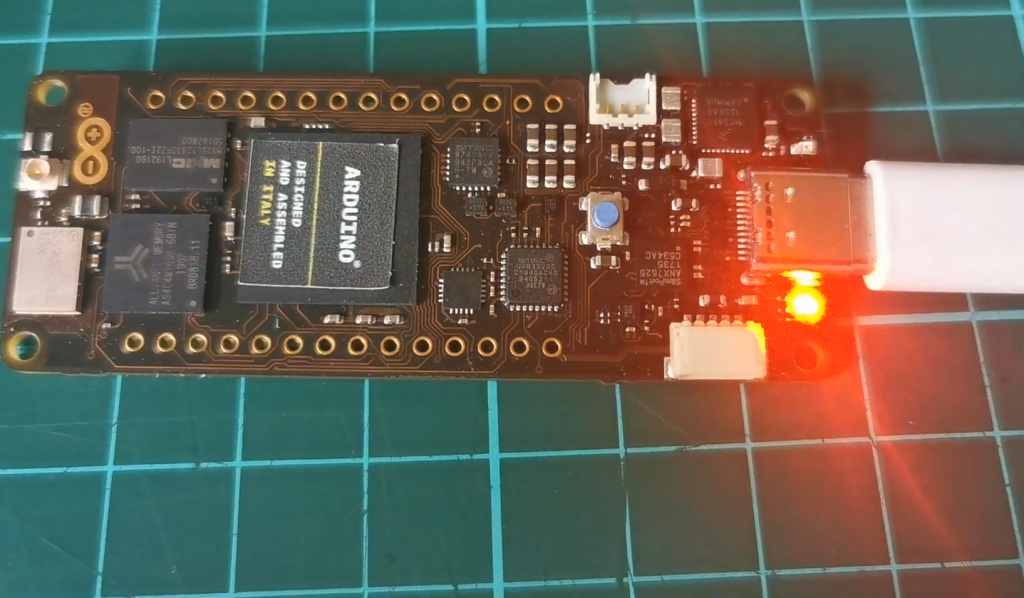
Technical Specifications:
- Microcontroller: Dual-core ARM Cortex-M7 and Cortex-M4;
- Clock Speed: Up to 480 MHz;
- RAM: 16MB;
- Flash Memory: 8MB;
- External Storage: microSD slot;
- Display: Arduino MKR Display connector;
- Connectivity: Ethernet, WiFi, and Bluetooth (BLE);
- USB: USB-C Multipurpose Connector;
- Power Supply: Li-Po battery management;
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V;
- GPIO Pins: Up to 37 (varies depending on use cases);
- Operating Temperature: -40°C to +85°C;
- Dimensions: 102mm x 25mm;
Two Parallel Cores
At the heart of the Arduino Portenta H7 lies its dual-core architecture. Featuring a powerful combination of an ARM Cortex-M7 and an ARM Cortex-M4 core, this microcontroller offers developers a unique blend of computational capability and efficiency.
The Cortex-M7 core, running at up to 480 MHz, is ideal for demanding tasks and real-time applications. It can handle complex algorithms, high-speed data processing, and more, making it suitable for applications like computer vision, machine learning, and robotics [2].
On the other hand, the Cortex-M4 core, with its lower power consumption, complements the Cortex-M7 beautifully. It is well-suited for low-power tasks, managing peripherals, and handling background operations, ensuring optimal power management and efficiency.
Graphics Accelerator
The Portenta H7 also boasts a built-in graphics accelerator, making it a capable platform for applications involving displays and graphical user interfaces (GUIs). This hardware accelerator significantly eases the burden on the CPU when rendering graphics, resulting in smoother and more responsive user experiences.
The presence of the Arduino MKR Display connector further enhances the board’s graphic capabilities. It allows for easy integration of displays, making it suitable for projects ranging from simple LCD screens to more complex touch-enabled displays.
A New Standard for Pinouts
One of the defining features of the Portenta H7 is its commitment to a new standard for pinouts. Arduino has made an effort to align the Portenta H7 with industry standards, providing compatibility with a wide array of shields and accessories.
The Portenta H7 follows the Arduino MKR form factor, which features a high-density connector that supports a variety of modules and accessories. This alignment with industry standards not only simplifies the process of finding compatible hardware but also fosters a thriving ecosystem of add-ons, ensuring that developers have access to the tools they need to bring their projects to life.
On-Board Connectivity
Connectivity is crucial in the world of IoT and embedded systems, and the Portenta H7 does not disappoint. It offers a range of onboard connectivity options, including Ethernet, WiFi, and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). These options open up a world of possibilities for IoT projects, enabling seamless communication and data transfer [3].
The Ethernet connection provides a stable and reliable way to connect the Portenta H7 to local networks and the internet, making it suitable for applications that require high-speed data transfer and low latency.
WiFi and BLE, on the other hand, cater to wireless communication needs. Whether you’re building a smart home device, a remote monitoring system, or a wearable gadget, the Portenta H7’s wireless capabilities should be enough.
USB-C Multipurpose Connector
Another standout feature of the Portenta H7 is its USB-C multipurpose connector. This versatile connector serves multiple functions, including power input, data transfer, and programming. Its inclusion simplifies the board’s power management and enhances its usability.
With USB-C, you can power the Portenta H7 using a wide range of power sources, from USB chargers to power banks, providing flexibility and convenience in various applications. Moreover, the USB-C connector supports high-speed data transfer, enabling quick and efficient programming of the board.
Multiple Options In One Board
One of the most impressive aspects of the Arduino Portenta H7 is its adaptability. It’s not a one-trick pony; it can adapt to various project requirements with ease. Whether you’re building a battery-powered IoT device, a machine learning project, or a robotics platform, the Portenta H7 can be configured to suit your needs [4].
Thanks to its modular architecture and rich set of interfaces, you can expand the Portenta H7’s capabilities by adding specialized shields and accessories. This adaptability makes it an excellent choice for both beginners and experienced developers, as it can grow with you as your skills and project requirements evolve.
Pinout Diagram
To better understand the Portenta H7’s adaptability and ease of use, let’s take a closer look at its pinout diagram. The board features a range of GPIO pins, analog inputs, UART, I2C, and SPI interfaces, as well as power and ground pins. This extensive set of pins allows you to connect sensors, displays, actuators, and other components seamlessly.
Here’s a brief overview of some key pin functions:
- Digital GPIO: These pins can be used for digital input or output, making them suitable for connecting LEDs, buttons, and other digital devices;
- Analog Inputs: Analog pins allow you to read analog signals from sensors, potentiometers, and other devices. They are essential for measuring variables such as temperature, light, or sound;
- UART, I2C, and SPI: These communication interfaces enable the Portenta H7 to connect with a wide range of devices, including sensors, displays, and other microcontrollers;
- Power and Ground: These pins provide the necessary voltage and ground connections for your components, ensuring proper operation [5];
By consulting the pinout diagram and referencing the Portenta H7’s documentation, you can easily configure the board to interact with the specific components required for your project, making it a versatile platform for a wide range of applications.
Additional I2C Port
As if the Portenta H7’s connectivity options weren’t extensive enough, it also features an additional I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) port. I2C is a popular communication protocol used in many embedded systems for connecting sensors, displays, and other peripherals [6].
The availability of an extra I2C port further enhances the board’s flexibility, enabling you to connect multiple I2C devices simultaneously without the need for complex wiring or additional hardware. This feature can be particularly advantageous in projects that demand a variety of sensors or require precise communication between multiple components.
Differences Between Portenta H7 & H7 Lite
The Arduino Portenta H7 and Portenta H7 Lite are two distinct variants of the Portenta H7 series. While they share certain core features, they also have significant differences that cater to different use cases and budgets.
1. Microcontroller Cores:
- Portenta H7: The Portenta H7 features a dual-core microcontroller architecture. It combines an ARM Cortex-M7 core (high-performance) and an ARM Cortex-M4 core (low-power);
- Portenta H7 Lite: The Portenta H7 Lite also utilizes a dual-core microcontroller architecture, consisting of an ARM Cortex-M7 core and an ARM Cortex-M4 core. This configuration is similar to the Portenta H7;
2. Clock Speed:
- Portenta H7: The Portenta H7’s microcontroller cores can operate at a clock speed of up to 480 MHz for the Cortex-M7 core;
- Portenta H7 Lite: The clock speed of the Portenta H7 Lite’s microcontroller cores is identical to that of the Portenta H7, with the Cortex-M7 core capable of running at speeds of up to 480 MHz;
3. RAM and Flash Memory:
- Portenta H7: The Portenta H7 is equipped with 16MB of RAM and 8MB of Flash memory. This ample memory capacity makes it suitable for applications requiring substantial computational resources and storage;
- Portenta H7 Lite: The Portenta H7 Lite shares the same memory specifications as the Portenta H7, featuring 16MB of RAM and 8MB of Flash memory;
4. Graphics Accelerator:
- Portenta H7: The Portenta H7 includes a built-in graphics accelerator, which enhances its capabilities for graphical user interface (GUI) applications and rendering graphics;
- Portenta H7 Lite: The Portenta H7 Lite, like its sibling, is equipped with a graphics accelerator. This feature is consistent across both models;
5. On-Board Connectivity:
- Portenta H7: The Portenta H7 offers a comprehensive set of onboard connectivity options, including Ethernet, WiFi, and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). It provides versatile communication capabilities for various IoT and embedded applications;
- Portenta H7 Lite: The Portenta H7 Lite, similar to the Portenta H7, provides Ethernet, WiFi, and BLE connectivity options. These options are essential for enabling wireless and wired communication in embedded systems [7];
6. USB-C Multipurpose Connector:
Both the Portenta H7 and H7 Lite feature a USB-C multi-purpose connector, which serves as the power input, data transfer, and programming interface. This USB-C connector enhances usability and simplifies power management.
7. Power Supply:
- Portenta H7: The Portenta H7 includes Li-Po battery management capabilities, allowing it to be powered by lithium-polymer batteries. This feature is valuable for portable and battery-powered applications;
- Portenta H7 Lite: The Portenta H7 Lite also supports Li-Po battery management, making it suitable for projects that require portable power sources;
8. Additional Features:
It’s important to note that both the Portenta H7 and H7 Lite models are compatible with a wide range of Arduino shields and accessories. This compatibility ensures that developers have access to an extensive ecosystem of hardware add-ons for expanding the capabilities of their projects.
9. Differences in Form Factor and Features:
One of the key differences between the Portenta H7 and H7 Lite is the form factor. The Portenta H7 Lite is designed in a smaller, more compact form factor compared to the Portenta H7. Additionally, the Portenta H7 Lite lacks the secondary connector and extra GPIO pins found on the Portenta H7.
Summing up, while the Portenta H7 and Portenta H7 Lite share several core features such as dual-core microcontrollers, clock speeds, memory specifications, graphics accelerators, on-board connectivity, USB-C connectors, and Li-Po battery support, there are some differences in form factor and the presence of additional connectors and GPIO pins.
The choice between these models should be based on the specific requirements of your project, with the Portenta H7 offering more expandability and the Portenta H7 Lite being a compact and cost-effective option.
Arduino Portenta H7: Use Cases
Here are some prominent use cases for the Arduino Portenta H7:
IoT Prototyping and Development:
The Portenta H7’s WiFi and Ethernet connectivity options make it an excellent choice for building IoT prototypes and projects. You can create smart home devices, environmental monitoring systems, and data loggers that connect to the internet and share data.
Machine Learning and Computer Vision:
The dual-core architecture, with a high-performance Cortex-M7 core, makes the Portenta H7 suitable for machine learning and computer vision applications. You can implement image recognition, object detection, and other AI tasks.
Robotics and Automation:
Robotics enthusiasts can use the Portenta H7 to build robots and automation systems. Its ample processing power, GPIO pins, and communication interfaces enable you to control motors, sensors, and actuators effectively.
Edge Computing:
The Portenta H7’s computational capabilities allow for edge computing applications where data processing occurs locally, reducing the need for continuous cloud connectivity. This is useful in scenarios where low latency and privacy are essential.
Interactive Art and Installations:
Artists and designers can leverage the Portenta H7 to create interactive art installations and exhibits. Its graphics acceleration and compatibility with various displays enable you to craft visually appealing and interactive experiences.
Education and Learning:
The Portenta H7 is an excellent educational tool for teaching electronics, programming, and IoT concepts. It’s beginner-friendly, and Arduino’s extensive community and documentation provide valuable resources for students and educators.
Wearable Technology:
With its compact size and low-power capabilities, the Portenta H7 is suitable for wearable technology projects. You can develop smart wearables like fitness trackers, health monitors, and even smart clothing [8].
Environmental Monitoring:
Use the Portenta H7 to build environmental monitoring systems that measure temperature, humidity, air quality, and more. These systems can be deployed in homes, industrial settings, or research applications.
Data Acquisition and Analysis:
The Portenta H7’s GPIO pins and communication interfaces enable data acquisition from various sensors and instruments. You can collect and analyze data for scientific research, industrial monitoring, or agricultural applications.
Prototyping and Proof of Concept:
For engineers and developers, the Portenta H7 serves as a powerful prototyping platform for testing ideas and concepts before moving to larger-scale production. Its compatibility with Arduino shields and accessories simplifies the prototyping process.
Low-Power Battery-Powered Devices:
The Portenta H7’s support for Li-Po batteries and low-power Cortex-M4 core makes it suitable for creating battery-powered, energy-efficient devices such as remote sensors or portable gadgets.
Communication Hubs:
You can use the Portenta H7 as a communication hub or gateway in IoT networks. It can aggregate data from multiple sensors and devices, process it locally, and transmit relevant information to the cloud or other endpoints.
Custom Industrial Control Systems:
In industrial settings, the Portenta H7 can be used to create custom control and monitoring systems. It can interface with industrial sensors, actuators, and control systems, providing flexibility in automation.
These use cases highlight the versatility of the Arduino Portenta H7, showcasing its adaptability to various projects across different domains.
Whether you are a hobbyist, student, researcher, or professional, the Portenta H7 offers a robust platform for bringing your creative and innovative ideas to life.
Arduino Portenta H7: Pricing and Availability
The Arduino Portenta H7, a high-performance board designed for industrial applications, is available at various price points depending on the version and retailer.
At the Arduino store, the Portenta H7 is priced at $45.60, while the Portenta H7 Lite Connected model is available for $82 or US$98.40.
On Amazon, the Arduino Portenta H7 is available, but the price is not specified. A bundle including the Portenta H7 and Vision Shield ETH is listed at $149.99.
The IoT-focused version was announced at CES 2020 for $99.99. Microcenter and Newark have the ABX00042 model listed with in-store only deals and a price of $106.45 respectively.
Elektor offers the Arduino Pro Portenta H7 at a regular price of $439, and Okdo lists the Arduino Portenta H7 Lite Connected for $107.99.
FAQ:
1. Is Portenta H7 good?
The Arduino Portenta H7 has received mixed reviews. Some users laud it as the best-embedded computing platform of 2022, praising its onboard crypto authentication chip which provides a high degree of tamper resistance. However, others have critiqued the lack of documentation about the multicore, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth features, as well as the device packaging.
2. How fast is Arduino Portenta H7?
The Arduino Portenta H7 is powered by a dual-core unit that features a 480 MHz ARM Cortex-M7 and a 240 MHz ARM Cortex-M44. This allows for tasks to run in parallel, with both cores communicating with one another4.
3. What is the use of Arduino Portenta H7?
The Arduino Portenta H7 is a versatile microcontroller board designed for a wide range of use cases.
Its primary uses include:
- IoT Prototyping: The Portenta H7 is well-suited for building IoT prototypes and devices. Its connectivity options, such as Ethernet, WiFi, and Bluetooth, enable you to create connected devices for home automation, environmental monitoring, and more;
- Machine Learning and AI: With its dual-core architecture and ample memory, the Portenta H7 can be used for machine learning, computer vision, and AI applications. It can handle tasks like image recognition, natural language processing, and data analysis;
- Robotics and Automation: The board’s GPIO pins, communication interfaces, and processing power make it suitable for robotics and automation projects. You can build robots, control sensors, and actuators, and create automation systems;
- Edge Computing: The Portenta H7 can be used for edge computing applications where data processing occurs locally, reducing the need for continuous cloud connectivity. This is useful for low-latency applications and privacy-sensitive tasks;
- Interactive Art and Displays: Artists and designers can use the Portenta H7 to create interactive art installations, displays, and exhibits with its graphics acceleration and compatibility with various displays;
- Education: The Portenta H7 serves as an educational tool for teaching electronics, programming, and IoT concepts. It is beginner-friendly and supported by Arduino’s extensive educational resources;
- Wearable Technology: Its compact size and low-power capabilities make it suitable for wearable technology projects, including fitness trackers, health monitors, and smart clothing;
4. How fast is the ADC in Portenta H7?
The analog-to-digital converter (ADC) requires approximately 1 microsecond (1 mega-sample per second or 1 Msps) to perform a single ADC conversion and store the result in the data array.
5. What is the fastest loop on Arduino?
The speed of a loop in Arduino can vary depending on the specific model and the complexity of the code being executed. However, in general, simple loops can be executed in microseconds. For more accurate measurements, consider using the micros() function in Arduino to measure the execution time of your loop.
6. What is the difference between Arduino Giga and Portenta H7?
While both the Arduino Giga R1 WiFi and the Arduino Portenta H7 are powerful boards, there are some key differences. The Giga R1 WiFi is designed more for makers, with a focus on multimedia and gaming applications. On the other hand, the Portenta H7 is designed for professional use in industrial applications.
7. How much power does a Portenta H7 use?
The usual power usage is approximately 5.00 volts and around 300 milliamperes, potentially surging to 400 milliamperes intermittently (this hasn’t been actively assessed yet but should be within the acceptable range for USB-C, similar to USB-A on any personal computer).
8. Is Arduino Portenta open source?
Yes, like all Arduino products, the Arduino Portenta H7 is open-source. This means that its design files and source code are freely available, allowing users to modify and build upon the hardware and software.
Useful Video: Portenta H7 LoRa Air Station | Product Review
References:
- https://makezine.com/products/boards/arduino-pro-portenta-h7/
- https://community.element14.com/products/roadtest/rv/roadtest_reviews/933/arduino_portenta_h7_1
- https://www.hackster.io/news/the-new-arduino-portenta-5ae687010500
- https://beebom.com/arduino-portenta-h7-module/
- https://www.circuitstate.com/news/portenta-h7-lite-is-a-stripped-down-version-of-arduino-pros-flagship-industrial-controller-board/
- https://store.arduino.cc/products/portenta-h7
- https://thinkrobotics.com/products/arduino-portenta-h7-online
- https://eu.mouser.com/new/arduino/arduino-portenta-h7/

