Did you know that enterprise IT teams spend nearly 30% of their troubleshooting time on mobile device management synchronization problems? When policies fail to sync properly, it can disrupt entire workflows and leave devices in a vulnerable state.
One particularly stubborn challenge appears when managed equipment loses its connection to the backend service. This specific synchronization failure manifests as a distinct numerical identifier that stops policy updates dead in their tracks.
The problem typically surfaces during routine synchronization attempts from device settings. Administrators notice failed sync attempts and specific messages in system logs indicating communication breakdowns.
At its core, this situation represents a broken trust relationship between the managed equipment and the management service. The connection cannot repair itself automatically, requiring manual intervention to restore proper functionality.
Understanding this particular synchronization failure is crucial for maintaining smooth operations in business environments. While it demands attention, proven solutions exist to get your equipment back on track quickly.
Key Takeaways
- This synchronization failure indicates a broken trust relationship with the management service
- The problem typically occurs during policy synchronization attempts
- Failed sync attempts and specific log messages are common symptoms
- Automatic remediation is not possible for this type of connection issue
- Device re-enrollment is typically required to resolve the underlying trust problem
- Proper diagnosis can prevent extended downtime in enterprise environments
- Understanding this failure helps maintain efficient mobile device management
Introduction to Intune Error Code -2016281112
The breakdown in communication between managed devices and backend services creates recurring headaches for IT professionals. This specific synchronization failure appears when equipment loses its connection to management platforms.
Overview of the Issue
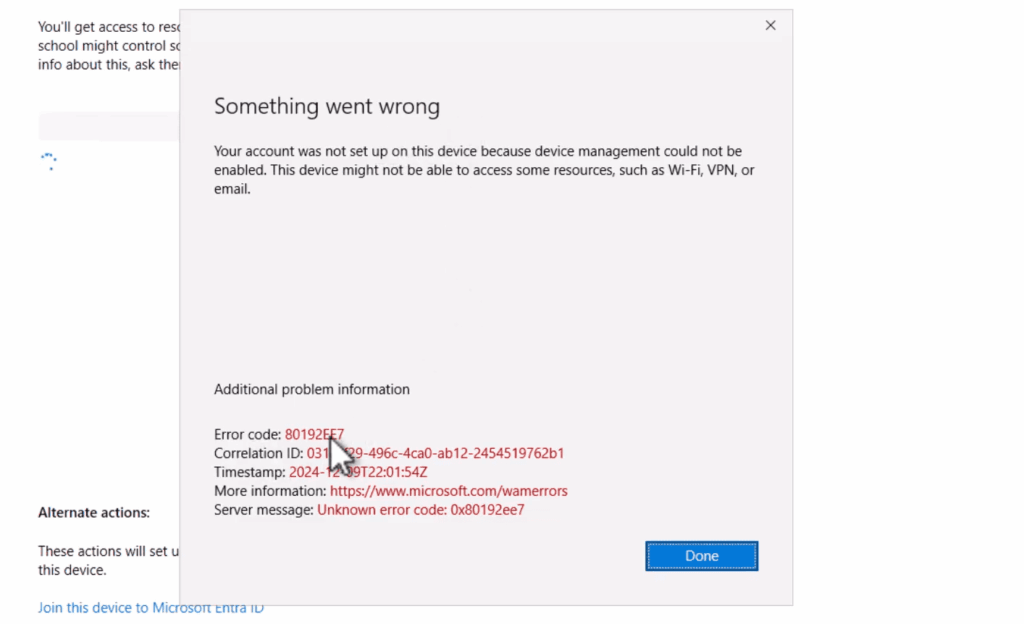
Users typically notice this problem when attempting to sync policies from their device settings. The interface displays a clear message: “Sync wasn’t fully successful.” This indicates immediate communication problems.
System event logs provide more detailed information. They record a specific event message: “MDM Session: OMA-DM message failed to be sent. Result: (Bad request (400)).” This shows the technical communication breakdown between the device and service.
This situation represents a trust relationship failure. It prevents normal mobile device management communication from occurring properly.
Relevance for IT Administrators
For IT teams managing Windows 10 and later equipment, this issue affects device compliance and policy application. Multiple devices can experience this problem simultaneously if underlying conditions aren’t addressed.
Prompt resolution maintains security compliance and ensures proper policy enforcement. Understanding this failure helps keep equipment properly managed within organizational infrastructure.
The error occurs frequently in enterprise environments. Devices become more susceptible under certain conditions that strain the trust relationship.
Understanding Microsoft Intune and Its Environment
The shift to remote work has accelerated the adoption of comprehensive device management platforms. Microsoft’s cloud-based solution provides centralized control over corporate equipment across diverse locations.
This service integrates seamlessly with the broader Microsoft ecosystem. It connects with Azure Active Directory and other Microsoft 365 tools for unified management.
Key Features and Benefits
Organizations gain powerful capabilities through this platform. Mobile device management ensures proper configuration across all enrolled equipment.
Conditional access policies help maintain security standards. Application management controls software deployment throughout the company environment.
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile Device Management | Centralized control over device settings | Uniform configuration across organization |
| Application Management | Software deployment and updates | Consistent application environment |
| Conditional Access | Security-based access rules | Enhanced protection for company data |
| Automated Enrollment | Streamlined device onboarding | Reduced IT administrative workload |
Trust relationships form the foundation of this management approach. Certificate-based authentication ensures secure communication between each device and the cloud service.
Regular synchronization maintains policy compliance across the entire device fleet. This continuous connection enables real-time monitoring and quick response to issues.
Identifying the Impact of intune error code -2016281112
Corporate devices experiencing this trust breakdown become isolated from critical management functions almost immediately. The policy synchronization failure means configuration changes made in the admin center won’t reach affected equipment. This creates potential security gaps that require urgent attention.
Compliance reporting becomes unreliable when this problem occurs. Administrators may see outdated status information because devices cannot communicate their current state accurately. This reduced visibility makes it difficult to maintain organizational standards.
Application deployment and software updates face significant disruptions. Critical security patches and necessary software may not reach the affected user devices, leaving them vulnerable. The management platform cannot push new applications or updates successfully.
End users experience direct consequences from this connection issue. They may lose access to company resources protected by conditional access policies. These policies typically require compliant devices for resource access.
The administrative burden increases significantly with this type of problem. Instead of automated management processes, IT teams must intervene manually to re-establish device trust. This creates additional workload and potential delays in resolution.
Understanding these impacts helps administrators prioritize resolution. The risks include security vulnerabilities, policy non-compliance, and reduced operational visibility. Prompt action prevents extended exposure to these potential threats.
Common Scenarios Leading to Error Occurrence
The trust breakdown doesn’t occur randomly but follows specific patterns in enterprise environments. Several everyday situations create the perfect conditions for this management communication failure.
Device Sync and Enrollment Issues
Equipment that stays offline for extended periods often develops this problem. When certificates expire during disconnection, the trust relationship cannot renew properly.
Incomplete enrollment processes leave devices in a partially registered state. This creates ongoing synchronization challenges that eventually manifest as communication failures.
Network infrastructure changes frequently trigger these issues. New proxy servers or firewall rules can interrupt the communication path between equipment and management services.
Certificate problems represent another common scenario. Authentication certificates may become invalid, corrupted, or mismatched over time.
| Scenario Type | Common Causes | Impact on Device |
|---|---|---|
| Extended Offline Periods | Certificate expiration during disconnection | Lost trust relationship |
| Incomplete Enrollment | Partial registration process | Unstable management connection |
| Network Changes | New proxy or firewall configurations | Communication path interruption |
| Certificate Issues | Invalid or corrupted authentication | Failed service communication |
Improper removal procedures create orphaned registration data. When equipment gets manually deleted without proper cleanup, subsequent sync attempts face conflicts.
Timing also plays a role in these situations. Sync attempts during service maintenance windows or backend availability issues can trigger the problem.
System Log Analysis and Error Message Insights
Event logs provide the clearest window into what’s happening when device management communication fails. These detailed records capture every interaction between your equipment and the management service.
When you encounter synchronization problems, the system’s diagnostic logs become your best friend. They contain specific messages that explain exactly why the communication broke down.
Decoding OMA-DM and Event Log Messages
Look for the DeviceManagement-Enterprise-Diagnostics-Provider log in Event Viewer. Navigate to the Admin section where management-related events are recorded.
The key message you’ll find states: “MDM Session: OMA-DM message failed to be sent. Result: (Bad request (400)).” This indicates the device tried to communicate but received a rejection.
OMA-DM stands for Open Mobile Alliance Device Management protocol. It’s the language devices use to talk with management services. The “400 Bad Request” response means the server couldn’t understand or accept the message.
Download the Intune Debug Toolkit for real-time monitoring. Its MDM eventlog monitor feature shows live management events as they occur.
Correlate these event log entries with Azure sign-in logs and device status reports. This helps you determine if the issue relates to authentication, network problems, or certificate errors.
Other messages appearing alongside the main event provide additional context. They help pinpoint whether the root cause involves credentials, connectivity, or trust relationships.
Network Connectivity and Configuration Issues
Network infrastructure serves as the invisible backbone supporting all device management communications. When this foundation becomes unstable, synchronization processes cannot complete successfully. The quality of your network connection directly impacts management operations.
Devices require specific network pathways to maintain trust relationships. They need uninterrupted access to management endpoints through proper ports and protocols. Without this reliable connection, communication attempts fail.
| Diagnostic Tool | Primary Function | Common Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Test-NetConnection | Verifies endpoint reachability | Port accessibility and latency issues |
| nslookup | DNS resolution testing | Name resolution failures |
| tracert | Network path analysis | Routing problems and bottlenecks |
Corporate proxy servers often create unexpected barriers. They might block management traffic even when general internet access works normally. Authentication requirements can interrupt automated sync processes.
“Network diagnostics reveal the hidden obstacles preventing successful device management. What appears as a trust issue often stems from basic connectivity problems.”
DNS resolution problems frequently mimic trust relationship failures. When devices cannot resolve management server names, communication requests fail immediately. Proper configuration ensures seamless access to essential services.
Firewall logs and proxy monitoring tools help identify blocked connections. Review these resources when sync operations cannot be completed. They provide crucial insights into network-level obstacles.
Certificate and Authentication Challenges
Digital certificates form the backbone of secure device management communications. When these authentication mechanisms fail, the trust relationship between equipment and management services breaks down completely.
Many synchronization problems occur when devices contain multiple certificates. The system might attempt to use an expired or incorrect certificate for authentication. Cleaning out invalid certificates often resolves the underlying connection issue.
MFA and User Credential Considerations
Multi-factor authentication requirements add another layer of complexity to device synchronization. When security controls in Entra ID aren’t satisfied during sync attempts, only basic device communication succeeds. User-specific policies fail to apply properly.
Azure sign-in logs clearly show these authentication failures. They indicate when accounts need additional identity verification. The solution typically involves clicking sync and completing the authentication prompt when it appears.
Proper certificate management prevents many of these challenges. Regularly check certificate validity and expiration dates. Implement alerts before certificates expire to maintain uninterrupted device access.
Monitoring certificate chains ensures devices maintain proper authentication credentials. This proactive approach helps avoid trust relationship breakdowns that disrupt management operations.
Troubleshooting Steps: Device Clean-up and Re-enrollment
Resolving persistent synchronization failures often demands a fresh start through comprehensive device re-enrollment processes. This approach establishes a new trust relationship between equipment and management services.

Script-Based Re-enrollment Procedures
Administrators can use automated scripts to streamline the cleanup process. These tools remove old registration data and prepare devices for fresh enrollment.
The script approach handles multiple cleanup tasks simultaneously. It targets registration records across different management systems. This method works efficiently for bulk device remediation.
Important warning: Script-based solutions are not officially supported. Use them at your own risk after thorough testing.
Manual Device Re-registration Strategies
Manual re-enrollment provides complete control over the cleanup process. Start by removing the device serial number from the admin portal.
Next, delete the corresponding registration object from the directory service. Finally, re-register the equipment through standard enrollment procedures.
Users simply enter their credentials during the fresh enrollment process. The system establishes new trust relationships automatically.
| Method | Best For | Time Required | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Script-Based | Multiple devices | 15-30 minutes | Medium |
| Manual Process | Single devices | 30-45 minutes | Low |
Verify cleanup completion by checking device status in admin portals. Schedule re-enrollment during low-usage periods to minimize user disruption.
Monitor the enrollment progress closely. Look for successful policy synchronization as the key success indicator.
Comparative Analysis of Similar Error Codes
When managing diverse device fleets, recognizing common error themes becomes essential for effective IT administration. Understanding how different platforms manifest similar problems helps streamline troubleshooting across your entire environment.
Apple MDM Agent vs. Windows Intune Errors
Both Windows and Apple management systems encounter comparable challenges. Network connectivity issues appear across platforms with similar symptoms. For example, Apple’s network connection lost error parallels Windows sync failures.
Application installation problems represent another universal challenge. Different platforms report these issues using distinct codes but share common resolution paths. Retrying installations often resolves the problem regardless of device type.
Authentication and token expiration affect all management systems. These backend issues can generate generic “unknown error” messages. The root cause typically involves expired credentials or service tokens.
| Error Type | Windows Manifestation | Apple Manifestation | Common Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network Connectivity | Sync failure with bad request | Connection lost/interrupted | Check network paths and retry |
| Application Installation | Install command failure | App not detected post-install | Verify installation and retry |
| Authentication Issues | Trust relationship failure | Unknown error with token problems | Renew credentials or tokens |
| Generic Failures | Various sync errors | Unspecified command failures | Basic retry and system checks |
This comparative approach helps administrators develop universal troubleshooting skills. Recognizing patterns makes problem-solving more efficient across different device versions and application types.
Reviewing Intune Debug Toolkit and Event Logs
Microsoft provides dedicated diagnostic utilities specifically designed for mobile device management challenges. The Intune Debug Toolkit offers specialized monitoring capabilities that enhance standard Windows event log viewing.
This powerful tool focuses on the DeviceManagement-Enterprise-Diagnostics-Provider event log. It provides real-time monitoring features that make troubleshooting more efficient.
| Feature | Standard Event Viewer | Intune Debug Toolkit |
|---|---|---|
| Real-time Monitoring | Manual refresh required | Live event streaming |
| Event Filtering | Basic search capabilities | Advanced filtering options |
| Management Focus | General system events | Device management specific |
| Export Capabilities | Basic log export | Structured data export |
Download the toolkit from Microsoft’s official documentation site. Installation requires administrator privileges on the target device.
Navigate to Applications and Services Logs > Microsoft > Windows > DeviceManagement-Enterprise-Diagnostics-Provider > Admin. This path reveals detailed management events.
Filter events by time range and specific identifiers to pinpoint synchronization problems. The toolkit’s enhanced interface simplifies this process significantly.
Export event logs for documentation or support cases. Regular monitoring helps catch issues before they impact users.
Leveraging Microsoft Documentation and External Resources
Successful IT administrators know that comprehensive documentation separates great troubleshooting from guesswork. When you encounter technical challenges, having the right reference materials can dramatically reduce resolution time.
The collective knowledge of the IT community provides invaluable support beyond official documentation. Community experts often share practical insights that complement formal support channels.
Useful External Links and References
Microsoft’s official documentation offers detailed information for specific technical issues. Their reference pages provide step-by-step guidance for various scenarios.
Community forums like Microsoft Tech Community host active discussions about common problems. Administrators share real-world experiences and proven solutions.
Expert blogs from recognized MVPs offer deep technical analysis. These resources often include advanced troubleshooting techniques and automation scripts.
| Resource Type | Primary Benefit | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Official Documentation | Authoritative reference information | Standard procedures and best practices |
| Community Forums | Real-world experience sharing | Uncommon scenarios and workarounds |
| Expert Blogs | Advanced technical insights | Complex troubleshooting and automation |
| Update Channels | Current feature information | Staying informed about platform changes |
Staying current requires following key community blogs and update channels. This proactive approach ensures you have the latest information when challenges arise.
Participating in user groups creates valuable networking opportunities. These communities often share knowledge about resolving specific error codes and similar issues.
Resolving Autopilot and Enrollment Issues
Sometimes the automated setup process hits a snag, creating a tricky situation for your device. When Autopilot enrollment fails, it can leave equipment in a confused state that triggers other problems later.
One common enrollment issue shows up as error 0x801C0003. This message means the system thinks your equipment is already installed and registered. The device gets stuck between registration steps.
Deleting Device Serial Numbers and Re-Registering
Fixing this requires a complete reset of the registration data. Start by removing the device serial number from the Intune admin center. This clears the old registration record.
Next, visit the Azure portal to delete the corresponding Entra ID object. This ensures no orphaned records remain in the directory service. Complete cleanup prevents future conflicts.
The final step involves re-registering the equipment with the Autopilot service. Your user can then restart the setup process by entering their credentials. The system will establish a fresh connection.
This straightforward approach resolves most duplicate enrollment situations. It gives your device a clean slate for proper management.
Addressing Licensing and VPP App Errors
When application deployment stalls, licensing issues often share the blame. Volume Purchase Program challenges create unique obstacles that affect both your device management and software distribution.
Token authentication problems can ripple through multiple systems simultaneously. An expired or invalid VPP token might prevent license assignment while also contributing to broader trust relationship failures.
Common licensing scenarios include:
- License retrieval failures indicating token synchronization needs
- Assignment problems when no licenses remain available
- License location issues requiring revocation and reassignment
These situations frequently occur alongside the specific synchronization challenge we’ve been discussing. Your equipment needs proper communication with management services before it can receive or report license status accurately.
Troubleshooting starts with verifying your VPP token validity and synchronization status. Ensure tokens properly connect to Apple Business Manager or Apple School Manager. Regular token updates prevent many licensing headaches.
Check available license counts and review assignment history. Identify whether you’re dealing with user-licensed versus device-licensed application types. This distinction affects how you reclaim and reassign licenses.
When licenses appear unavailable, consider reclaiming them from inactive user accounts. Sometimes purchasing additional licenses becomes necessary for growing organizations.
Remember that resolving underlying trust issues often clears the path for licensing solutions. A device with proper management communication can successfully receive its assigned applications and licenses.
Application Installation and Update Troubleshooting
Getting applications properly deployed across your managed Windows equipment often reveals deeper management challenges. What appears as simple software installation problems can actually signal underlying communication issues between devices and management services.
Handling 32-bit vs. 64-bit App Installations
Modern Windows devices frequently reject 32-bit applications. This creates specific installation failures that require careful attention. You must identify the correct application type before deployment.
When an installation attempt fails, check whether you’re trying to deploy incompatible software. The system might block 32-bit applications on 64-bit-only equipment. Always verify architecture requirements for each application version.
| Error Scenario | Common Cause | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| 32-bit app rejection | Device architecture mismatch | Deploy 64-bit application version |
| Update failure reporting | Sync delay or trust issue | Verify device communication status |
| App not detected post-install | Incorrect detection rules | Review and adjust detection method |
Application detection problems often stem from simple configuration issues. Your management platform might show an application as already installed when it’s actually missing. Alternatively, successfully installed software might not appear in reports.
Version mismatch scenarios typically indicate reporting delays rather than actual installation problems. When device communication suffers, application status updates cannot reach your admin console promptly. Resolving sync issues often clears these false alerts.
Configure robust detection rules that check multiple installation indicators. Look for registry entries, file system locations, and installed programs data. This multi-layered approach reduces false negatives in application reporting.
Implementing Preventative Measures and Best Practices
Building strong prevention habits saves countless hours of troubleshooting down the road. A consistent maintenance routine keeps your device fleet healthy and responsive to management commands.
Regular Monitoring and Maintenance Tips
Set up automated alerts for devices that haven’t checked in within expected timeframes. Review sync status dashboards daily to catch communication issues early.
Certificate lifecycle management is crucial for uninterrupted service. Monitor expiration dates and test deployment before certificates expire.
- Verify management URLs remain accessible from all network locations
- Test proxy configurations regularly to ensure they stay current
- Establish maintenance windows for system updates and health checks
Keep your policy configuration simple and test changes in pilot groups first. Gradual rollout strategies prevent widespread issues.
Proper device retirement procedures prevent orphaned records. Always remove equipment from management services when it’s no longer in use.
Teach users basic troubleshooting steps they can attempt before contacting support. Early recognition of sync problems leads to faster resolution.
Leverage reporting analytics to identify trends indicating emerging issues. Proactive remediation keeps your entire system running smoothly.
Conclusion
When synchronization failures occur, having a systematic approach to troubleshooting becomes essential for maintaining operational continuity. The specific error code we’ve discussed represents a trust relationship breakdown between your device and the management service.
Remember that re-enrollment typically resolves this issue completely. The knowledge gained from this specific scenario applies to many related challenges in your device management system.
Implementing preventative measures discussed throughout this article will minimize future occurrences. Device management involves complex interconnected components, making thorough understanding crucial for IT administrators.
Leverage the Microsoft community and official documentation when facing challenging scenarios. These resources provide ongoing support for maintaining healthy management operations.

