In the world of cable connections, there exists a seemingly endless array of options, each boasting its own set of advantages and capabilities. However, when it comes to coaxial cables, two contenders reign supreme: RG11 and RG6. These two formidable forces are often compared, analyzed, and debated among audiovisual enthusiasts, leaving many to wonder, “What’s the difference?” If you’ve ever found yourself pondering this very question, fear not, this guide is about to embark on an illuminating journey through the realm of coaxial cables. Prepare to have your mind expanded as this guide will unravel the mysteries of RG11 and RG6, unlocking the secrets that lie within their sturdy, cable-clad exteriors.
How is Coaxial Cable Constructed?

The inner conductor is typically made of copper or aluminum and serves as the central core that carries the signal. It is surrounded by a layer of dielectric material, which acts as an insulator and helps to maintain the integrity of the signal by preventing energy loss or leakage.
The outer conductor, also known as the shield, is made of metal braiding or foil and serves as a barrier between the inner conductor and outside interference. This shield provides protection against EMI from external sources and also prevents the signal from interfering with other electronic devices.
The final layer is the jacket, which encases the entire cable and protects it from physical damage such as moisture, heat, or abrasion. The material used for the jacket can vary depending on the intended use of the cable. For example, cables used in outdoor environments may have a thicker and more durable jacket compared to those used indoors.
Overall, the construction of coaxial cable is crucial in ensuring efficient and reliable transmission of signals while also protecting against external interference. The careful selection and design of each component play a significant role in the overall performance of the cable. So, it is essential to choose high-quality coaxial cables for optimal results [1].
Applications of Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable has a wide range of applications in various industries, including telecommunications, broadcasting, and internet connectivity. It is commonly used for high-speed data transmission, such as in cable television and internet networks.
In the telecommunications industry, coaxial cables are used to transmit both analog and digital signals for telephone networks. Due to its ability to carry a vast amount of data with minimal loss, coaxial cable is also used for long-distance communication via submarine cables.
Another significant application of coaxial cable is in the field of broadcasting. It is commonly used to transmit TV and radio signals, ensuring high-quality audio and video transmission without interference.
In recent years, coaxial cable has also found widespread use in internet connectivity. It is a popular choice for cable internet services due to its ability to handle high-bandwidth data transmission effectively. Additionally, coaxial cable is also used in local area networks (LANs) for connecting computers and other devices.
With the continuous evolution of technology, the demand for efficient and reliable communication has only increased. As a result, the use of coaxial cables will continue to expand in various industries, making it an integral part of modern-day communication systems. So, understanding the construction and applications of coaxial cable is essential for anyone working in these industries [2].

RG6 vs RG11: Similarities And Differences
Attenuation And Compensating for It
Similar to other types of communication cables, both RG6 and RG11 come with their specifications and limitations when it comes to attenuation. Attenuation refers to the loss of signal strength as it travels through a cable. This can be caused by various factors such as distance, interference, and the quality of the cable itself.
Both RG6 and RG11 are designed to minimize attenuation and maintain signal integrity, especially for long-distance transmissions. However, RG11 is known to have significantly lower attenuation compared to RG6 due to its larger diameter and thicker insulation. This makes it more suitable for longer cable runs and higher frequency signals.
Signal Loss and Distance
As mentioned earlier, attenuation can cause signal loss which results in a weaker and sometimes distorted signal at the receiving end. For both RG6 and RG11, the amount of signal loss increases with distance. However, due to its larger size and lower attenuation, RG11 can maintain a stronger signal over longer distances compared to RG6.
Flexibility and Durability
When it comes to flexibility and durability, RG6 is known to be more flexible and easier to work with compared to RG11. This is because it has a smaller diameter and thinner insulation, making it more pliable. On the other hand, RG11’s larger size and thicker insulation make it more rigid and less flexible.
Price and Availability
In terms of pricing, RG6 is generally more affordable compared to RG11. This is because it requires less material to manufacture and is commonly used in residential installations. On the other hand, RG11 is usually more expensive due to its larger size and specialized use in commercial or industrial settings.
Applications and Usage
Both RG6 and RG11 have their specific applications and usage. RG6 is commonly used for residential installations such as cable TV, internet, and telephone services. It can also be used for smaller commercial or industrial setups that require lower-frequency signals. On the other hand, RG11 is designed for high-frequency applications and longer-distance transmissions. It is commonly used in larger commercial or industrial installations such as satellite communications and CCTV systems [3].

RG11 vs. RG6 Coaxial Cable: Which One Is Best?
Of course, it depends on what you’re using it for
When it comes to choosing between RG11 and RG6 coaxial cables, the decision ultimately relies on your specific needs and requirements. RG11 cables, with their larger diameter and lower attenuation, are typically used for longer cable runs and applications that demand higher signal strength. On the other hand, RG6 cables, with their smaller diameter and flexibility, are commonly used for shorter cable runs and applications that require flexibility and ease of installation. It is important to consider factors such as signal quality, distance, and installation requirements when making the right choice between RG11 and RG6 coaxial cables. By understanding the nuances and differences between these two types of cables, you can ensure optimal performance and reliability for your specific use case.
RG59 is for antennas, not cable TV
One common misconception is that RG59 coaxial cables can be used interchangeably with RG6 or RG11 cables for cable TV applications. However, this is not the case. While all three types of cables may look similar on the outside, they have distinct differences in terms of their inner conductor size and shielding characteristics. RG59 cables are primarily designed and used for antenna installations, not for cable TV. Using RG59 cables for cable TV can result in poor signal quality and disruptions to your viewing experience. It is best to stick with the appropriate type of coaxial cable for each specific application.
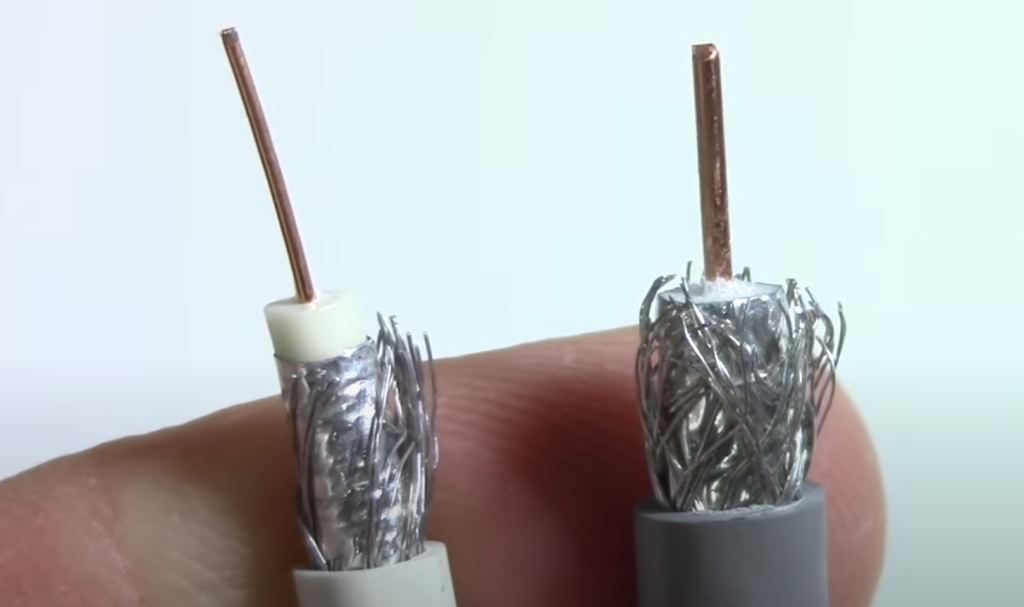
RG11 is only for special uses
Due to its larger diameter and higher signal strength capabilities, RG11 coaxial cable is typically used for specialized applications such as long-distance runs, underground installations, and commercial or industrial setups. Residential users may not necessarily need the added features of an RG11 cable and can opt for the more affordable and flexible RG6 cables instead. However, there are some cases where using RG11 cables for residential purposes may be beneficial, such as in areas with weaker signal strength or for future-proofing in case of future upgrades.
How to maintain Coaxial Cables?
Coaxial cables are widely used in various industries for transmitting signals such as television, internet, and telephone communication. They consist of a central conductor wire surrounded by an insulating layer, followed by a metal shield and an outer plastic jacket. These cables require proper maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Here are some tips for maintaining coaxial cables:
Regularly check for physical damage:
It is crucial to regularly inspect the cables for any indications of physical damage, including cuts, dents, or bends. These issues can significantly impact the transmission of signals, leading to potential disruptions or data loss. Therefore, it is recommended to promptly address and repair any damaged cables or replace them as necessary to ensure uninterrupted and efficient signal transmission.

Keep them away from heat sources:
Coaxial cables, commonly used for transmitting signals, are not designed to withstand high temperatures. When exposed to heat sources such as heaters or direct sunlight, these cables can melt or become brittle over time. To ensure their longevity and proper functioning, it is important to keep them away from any potential heat sources that could cause damage. Taking this precautionary measure will help maintain the integrity and reliability of your coaxial cables.
Avoid tight bends:
Secure connections:
To ensure optimal performance, it is crucial to double-check that all connections are securely fastened, paying special attention to the ends where the cables are connected to devices. Loose connections not only have the potential to result in signal loss but can also lead to interruptions in the transmission, impacting the overall efficiency and reliability of the system. Therefore, taking the time to properly secure all connections is a worthwhile investment in maintaining a seamless and uninterrupted experience.

FAQ
Which is better: RG6 or RG11?
- RG6 and RG11 are two types of coaxial cables commonly used for transmitting video, audio, and data signals.
- Both cables have a similar design with an inner conductor surrounded by insulating material, a braided shield, and an outer jacket.
- The main difference between the two is their physical size and maximum transmission distance.
- RG6 has a thinner diameter and is more flexible, making it suitable for shorter distances up to 200 feet.
- On the other hand, RG11 has a larger diameter and thicker shielding, allowing it to transmit signals over longer distances of up to 500 feet without any loss in quality.
- In terms of price, RG6 is generally less expensive than RG11 due to its smaller size and lower materials cost.
- Ultimately, the choice between RG6 and RG11 depends on your specific needs and budget, but both cables are suitable for most residential and commercial applications.
- For shorter distances or tight spaces, RG6 may be the better option, while for longer distances or higher bandwidth needs, RG11 may be a more reliable choice.
How do I choose the right coaxial cable for my needs?
To choose the right coaxial cable, there are a few key factors to consider. First, determine the type of signals you need to transmit (video, audio, data) and their required bandwidth. This will help determine the cable’s frequency range and transmission capabilities.
Next, consider the distance over which these signals need to be transmitted. If it is a shorter distance, RG6 may suffice, but for longer distances or higher bandwidth needs, RG11 may be a better option.
Another important factor is the environment in which the cable will be installed. For outdoor or harsh environments, choose a cable with thicker shielding to protect against interference and damage. Additionally, check for compatibility with your equipment and ensure that the cable meets industry standards such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or NEC (National Electrical Code).
Lastly, consider your budget and weigh the cost versus performance of different cable options. It may be worth investing in a higher-quality cable for critical or long-term use, but for temporary installations or basic needs, a more affordable option may suffice.
What is the difference between a coaxial cable and an HDMI cable?
While both coaxial and HDMI cables are used for transmitting audio and video signals, they differ in their design and capabilities. A coaxial cable has an inner conductor surrounded by insulating material, while an HDMI cable has 19 individual pins within a single plug. This allows HDMI to transmit higher-quality digital signals with more data channels compared to coaxial cables, which are limited to analog or lower-quality digital signals.
Additionally, HDMI cables have a specific orientation and must be plugged in correctly for proper signal transmission, while coaxial cables can be connected in any direction. Lastly, HDMI cables typically have a shorter maximum transmission distance of up to 50 feet, whereas coaxial cables can transmit over longer distances without any loss in quality.
Overall, HDMI cables are better suited for connecting devices like TVs and gaming consoles, while coaxial cables are better for longer distances or connecting to cable/satellite boxes. It is also worth noting that HDMI cables are typically more expensive than coaxial cables due to their advanced capabilities.
Can I use a splitter with a coaxial cable?
Yes, you can use a splitter with a coaxial cable to split the signal into multiple outputs. This is commonly done when connecting multiple devices (such as TVs or modems) to a single source, such as a cable/satellite box or antenna. However, it’s important to note that using a splitter may result in some signal loss and potentially impact the overall quality of the transmitted signal. To minimize this loss, use high-quality splitters and ensure that all connections are secure and properly terminated.
Additionally, some cable providers may have restrictions on using splitters, so it’s best to check with your provider before installing one. In some cases, using a dedicated coaxial cable for each device may be a better option to avoid signal degradation. Overall, it’s best to weigh the pros and cons before using a splitter and ensure that it is properly installed for optimal performance.
What are the uses of RG6 and RG11 cable?
RG6 and RG11 cables have a variety of uses in both residential and commercial settings. Some common applications include:
- Connecting cable or satellite boxes to TVs for receiving digital TV signals.
- Connecting modems to provide internet access through a cable provider.
- Connecting security cameras for surveillance systems.
- Connecting antennas for over-the-air broadcast reception.
- Transmitting audio signals, such as from a sound system to speakers.
- Transmitting video signals, such as from a DVD player to a TV.
Additionally, these cables can also be used for other data or communication purposes in industries like telecommunications and networking. The specific use of the cable will depend on its capabilities and the equipment it is being connected to. It’s important to research and choose the right cable for your specific needs to ensure optimal performance. Overall, RG6 and RG11 cables are versatile and widely used in various industries for their reliable transmission of signals over long distances. So whether you need to connect a TV or set up a complex network, these cables have got you covered.
Can you go from RG6 to RG11?
Yes, you can go from RG6 to RG11 cable by using a coupler or adapter. This allows for the connection of two cables of different types or sizes. For example, if you have a longer distance to cover and originally used RG6 but now need to switch to RG11 for better performance, you can use a coupler or adapter to seamlessly connect the two cables. Keep in mind that using a coupler may result in some signal loss, so it’s best to use high-quality ones and ensure proper installation for optimal performance. Additionally, it’s important to check the compatibility of your equipment with both types of cables before making the switch.
Conclusion Paragraph
In conclusion, coaxial cables play a crucial role in transmitting audio and video signals in various industries. When choosing the right cable for your needs, consider factors such as frequency range, distance, environment, compatibility, and budget. Understand the differences between coaxial and HDMI cables to determine which one is best suited for your specific devices and applications. Remember that using a splitter with a coaxial cable is possible but may result in signal loss, so it’s best to research and weigh the pros and cons before installation. Lastly, RG6 and RG11 cables have many uses and can be easily connected through a coupler or adapter if needed. By understanding the capabilities of these cables, you can make an informed decision and ensure optimal performance for your audio and video transmission needs.
Useful Video: RG6 vs. RG11 – How Your Coaxial Cable Impacts TV Reception
References:
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/coaxial-cable
- https://www.galaxywire.com/applications/coaxial-cable/
- https://www.tutorialspoint.com/difference-between-rg6-and-rg11

